Gaining Organizational Adoption: Strategically Pacing the Deployment of Digital Innovations – study of how entrepreneurs promoted the adoption of their new technologies, conducted by a researcher embedded in a digital health accelerator. Two approaches were found: an embedded approach where entrepreneurs engage deeply with customers to identify and develop use cases and market-centric approach where entrepreneurs systematically study the market before engaging with customers. The most successful entrepreneurs used strategic pacing which meant (1) concealing functionalities that may threaten stakeholders in an adopting organization, (2) restraining claims that a use case could displace or substitute for the work conducted by some members of an adopting organization and (3) adjusting the speed of introduction by customer organization.
The Evolution of Technology – explores four different perspectives that drive the variation, selection and retention of technologies.
- Technology Realist – technical factors such as performance are the main drivers
- Economic Realist – economic factors including R&D investment and scale are the main drivers
- Cognitive Interpretivist – in contrast to technology realism which assumes that cognitive representations of a technology aligns with the artifact itself, it assumes that there are different cognitive interpretations of a technology which then drive evolution.
- Social Constructionist – social factors such as power and networks are the drivers
Shaping Nascent Industries: Innovation Strategy and Regulatory Uncertainty in Personal Genomics – explores how new ventures in personal genomics managed regulatory uncertainties. It introduces the idea of regulatory co-creation which refers to iterative engagement with
regulators to shape standards.
Breakthrough invention and problem complexity: Evidence from a quasi-experiment – explores how the Google breakthrough AlphaGo has affected how technologists formulate questions in Stack Overflow. The study claims that the questions posed are of higher complexity after such a breakthrough invention. One implication of this is that although breakthroughs can be leveraged to create innovations, it may not be straightforward given the coordination required to manage such emerging complexities.
A Knowledge Recombination Perspective of Innovation: Review and New Research Directions – a nice review of knowledge recombination that takes into account the following:
- the features of an individual knowledge components (e.g. newness, context specificity)
- the interactions among a set of knowledge components (e.g. breadth vs. depth, modularity, networks)
- the architecture design from their recombination
- the outcomes of the recombination process in terms of novelty and usefulness
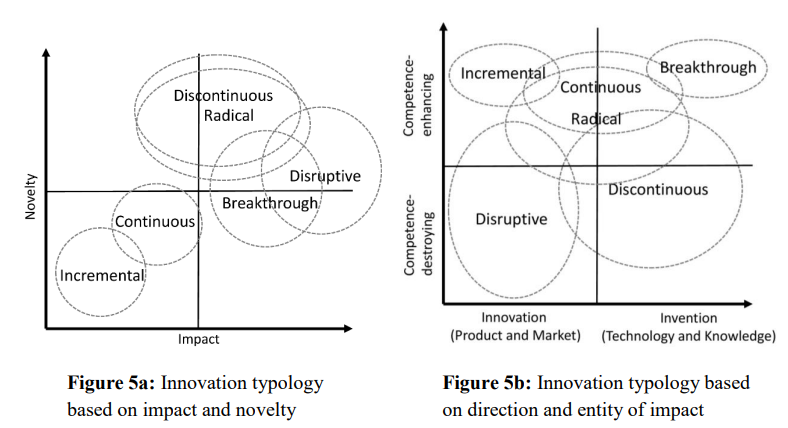
Revisiting innovation typology: A systemic approach – disentangles the various terms used to describe innovation such as radical, discontinuous, breakthrough and disruptive innovation